| dc.contributor.author | Chow, Alan-Michael D. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Shin, Jeonghwa | |
| dc.contributor.author | Wang, Hongwu | |
| dc.contributor.author | Kellawan, Jeremy Mikhail | |
| dc.contributor.author | Pereira, Hugo M. | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2022-09-02T20:32:40Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2022-09-02T20:32:40Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2022-03-18 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Chow A-MD, Shin J, Wang H, Kellawan JM and Pereira HM (2022) Influence of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Dosage and Associated Therapy on Motor Recovery Post-stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Aging Neurosci. 14:821915. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2022.821915 | en_US |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/11244/336522 | |
| dc.description.abstract | Purpose: (1) To determine the impact of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) applied alone or combined with other therapies on the recovery of motor function after stroke and (2) To determine tDCS dosage effect. | en_US |
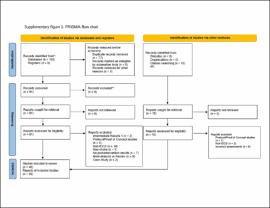
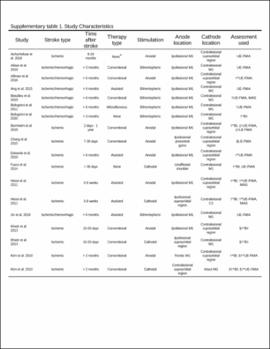
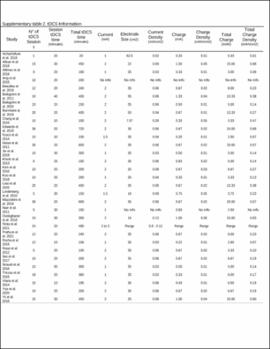
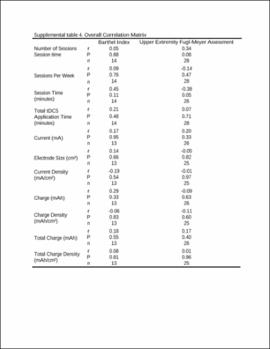
| dc.description.abstract | Methods: Randomized controlled trials comparing the effects of tDCS with sham, using the Barthel Index (BI), the upper and lower extremity Fugl–Meyer Assessment (FMA), and the Modified Ashworth Scale (MAS), were retrieved from PubMed, Medline (EBSCO), and Cumulative Index to Nursing and Allied Health Literature (CINAHL) from their inception to June 2021. Calculations for each assessment were done for the overall effect and associated therapy accounting for the influence of stroke severity or stimulation parameters. | |
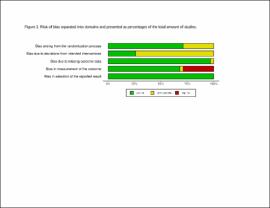
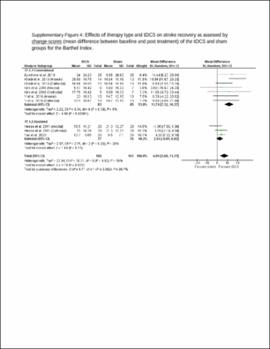
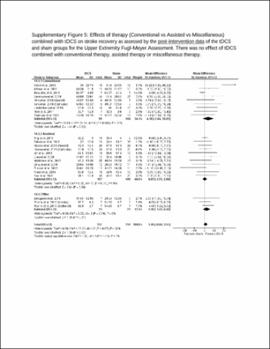
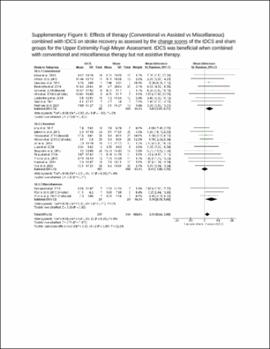
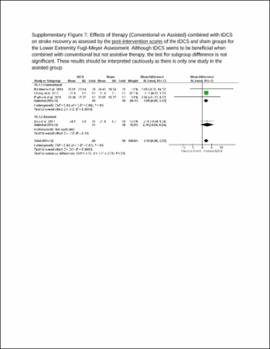
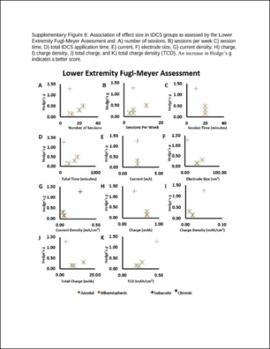
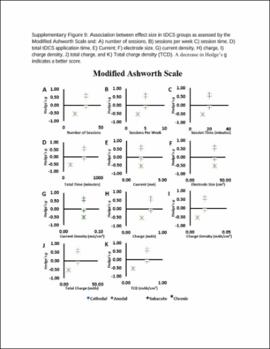
| dc.description.abstract | Results: A total of 31 studies involving metrics of the BI, the upper extremity FMA, the lower extremity FMA, and the MAS were included. tDCS combined with other therapies was beneficial when assessed by the BI (mean difference: 6.8; P < 0.01) and these studies typically had participants in the acute stage. tDCS effects on the upper and lower extremity FMA are unclear and differences between the sham and tDCS groups as well as differences in the associated therapy type combined with tDCS potentially influenced the FMA results. tDCS was not effective compared to sham for the MAS. Stimulation types (e.g., anodal vs. cathodal) did not influence these results and dosage parameters were not associated with the obtained effect sizes. Conventional therapy associated with tDCS typically produced greater effect size than assisted therapy. The influence of stroke severity is unclear. | |
| dc.description.abstract | Conclusion: Potential benefits of tDCS can vary depending on assessment tool used, duration of stroke, and associated therapy. Mechanistic studies are needed to understand the potential role of stimulation type and dosage effect after stroke. Future studies should carefully conduct group randomization, control for duration of stroke, and report different motor recovery assessments types. | |
| dc.description.abstract | Systematic Review Registration: [https://www.crd.york.ac.uk/PROSPERO/], identifier [CRD42021290670]. | |
| dc.description.sponsorship | Financial support was provided by the University of Oklahoma Libraries’ Open Access Fund. | en_US |
| dc.language | en_US | en_US |
| dc.rights | Attribution 4.0 International | * |
| dc.rights.uri | https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ | * |
| dc.subject | brain stimulation | en_US |
| dc.subject | tDCS | en_US |
| dc.subject | stroke | en_US |
| dc.subject | Barthel Index | en_US |
| dc.subject | Fugl-Meyer | en_US |
| dc.subject | Ashworth Scale | en_US |
| dc.subject | rehabilitation | en_US |
| dc.title | Influence of Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation Dosage and Associated Therapy on Motor Recovery Post-stroke: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis | en_US |
| dc.type | Article | en_US |
| dc.description.peerreview | Yes | en_US |
| dc.identifier.doi | doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.821915 | en_US |
| ou.group | Dodge Family College of Arts and Sciences::Department of Health and Exercise Science | en_US |