| dc.contributor.author | Harter, Zachery J. | |
| dc.contributor.author | Riddle, Jonathan | |
| dc.contributor.author | Chronister, Justin | |
| dc.contributor.author | Vassar, Matt | |
| dc.date.accessioned | 2020-04-14T16:12:32Z | |
| dc.date.available | 2020-04-14T16:12:32Z | |
| dc.date.issued | 2019-02-22 | |
| dc.identifier | ouhd_harter_evaluationofindustrypayments_2019 | |
| dc.identifier.citation | Harter, Z. J., Riddle, J., Chronister, J., & Vassar, M. (2019, Feb. 22). Evaluation of industry payments and financial conflict of interest disclosures among task force authors of Endocrine Society clinical practice guidelines. Poster presented on Research Day at the Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences, Tulsa, OK. | |
| dc.identifier.uri | https://hdl.handle.net/11244/323839 | |
| dc.description.abstract | Introduction: Clinical practice guidelines are considered the gold standard for disease management and treatment. Industry payments to guideline authors may influence their clinical recommendations, potentially resulting in medical and/or financial consequences to patients. | |
| dc.description.abstract | Research Question: Determine the extent Endocrine Society guideline authors receive industry payments and report financial conflicts of interest in adherence to the Physician Payments Sunshine Provision of the Affordable Care Act. | |
| dc.description.abstract | Study Design: Cross-sectional analysis of all clinical practice guidelines published by the Endocrine Society since the Sunshine Provision mandate. | |
| dc.description.abstract | Methods: We searched the Endocrine Society's website for clinical guidelines published between January 2014 and December 2017. Identified guideline authors were independently searched by two investigators on the Open Payments Database. Received payments were extracted and statistically analyzed (excluding food/beverage payments). Payments were cross-referenced with corresponding author disclosure statements. | |
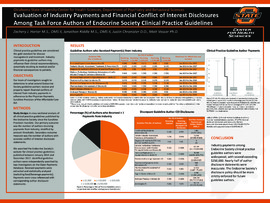
| dc.description.abstract | Results: Of the 57 evaluable guideline authors, 34 authors (59.6%) received at least one industry payment. Of these authors, thirty-three (57.89%) received ≥ $1,000, twenty-six (45.61%) ≥ $10,000, twenty-two (38.60%) ≥ $50,000, and twenty-one (36.84%) ≥ $100,000. Sixteen authors (28.07%) received ≥ $250,000 in industry payments. Median total payments were $4,060 (interquartile range [IQR] $0-263,264.23). Twenty-seven (47.37%) financial disclosure statements were inaccurate. Median payment (minus food/beverage) for inaccurate disclosures were $28,523.93 (IQR $5,714-94,418.02), with a payment total of $2,870,485.27. | |
| dc.description.abstract | Conclusion: Industry payments among Endocrine Society clinical practice guideline authors were widespread, with several exceeding $250,000. Nearly half of author disclosure statements were inaccurate. The Endocrine Society's disclosure policy should be more strictly enforced for future guideline authors. | |
| dc.format | application/pdf | |
| dc.language | en_US | |
| dc.publisher | Oklahoma State University Center for Health Sciences | |
| dc.rights | The author(s) retain the copyright or have the right to deposit the item giving the Oklahoma State University Library a limited, non-exclusive right to share this material in its institutional repository. Contact Digital Resources and Discovery Services at lib-dls@okstate.edu or 405-744-9161 for the permission policy on the use, reproduction or distribution of this material. | |
| dc.title | Evaluation of industry payments and financial conflict of interest disclosures among task force authors of Endocrine Society clinical practice guidelines | |
| osu.filename | ouhd_harter_evaluationofindustrypayments_2019.pdf | |
| dc.type.genre | Presentation | |
| dc.type.material | Text | |